- Welcome to Steroiduck -
We’re so happy you’re here! Whether you’re just starting bodybuilder or you’re a advanced player, we’ve got you covered with a trusted selection of top-quality steroids — from injectables and oral tablets to SARMs and more. Available mainly in USA and Canada, but with free worldwide delivery! You can shop confidently no matter where you are. Thanks for stopping by! We’re excited to help you get stronger, push harder, and crush your goals together.
Blog
Purchase Anabolic Steroids Online
Over 100+ Top Quality Anabolic Steroids & SARMS and More
Highest Quality
High quality steroids and SARMs are our top priority. We ensure that every supplement in our shop meets the highest standards. Your health deserves nothing less than the best, and that's exactly what you're going to find in our store. Buy steroids USA today!
Delivery Guaranteed
Your bodybuilding goals won’t wait, and neither should you. With delivery available across the USA, we’ll ensure your package arrive promptly at your doorstep, every time.
Laboratory Tested
Your health deserves the best, and we deliver just that. Every supplement and SARM in our store undergoes rigorous testing in state-of-the-art laboratories. We're not just talking about basic checks – our products are put through the wringer to ensure purity, potency, and safety. Buy Steroids in the USA and Canada with Steroiduck!
Maximum Benefits
Shop with our trusted bodybuilding steroids store in the USA and Canada to achieve maximum benefits and the best results. We offer top-quality tablets, injectables, HGH, SARMS, and more!
24/7 Support
No matter if you need advice, assistance, or have any questions or concerns, we are here for you 24/7. Our live chat is always available for you!
Anabolic Steroids for Sale Online at Steroiduck
Steroiduck is your reliable source for anabolic steroids, injectables, tablets, SARMs, and more. We cater to bodybuilders and fitness enthusiasts with proven, high-quality products. Our selection is available across the USA, offering trusted options for muscle growth, strength, and performance. Shop with confidence and achieve your fitness goals today.
What Are Steroids?
Steroids, also known as anabolic-androgenic steroids (AAS), are synthetic derivatives of testosterone, the primary male sex hormone. These compounds are designed to mimic the effects of naturally occurring testosterone, enhancing muscle growth (anabolic effects) and promoting male physical traits (androgenic effects).
In the context of sports and bodybuilding, anabolic steroids are primarily used to increase muscle mass, improve strength, and accelerate recovery times. Beyond their athletic applications, steroids are also used in medical settings to treat conditions such as delayed puberty, muscle-wasting diseases, and severe burns.
How do Steroids Work?
Steroids work by binding to androgen receptors in muscle cells, which triggers a cascade of biological processes. This interaction enhances protein synthesis, the process by which muscles repair and grow after stress, such as intense workouts.
At the same time, steroids reduce the breakdown of proteins, promoting a state of anabolic dominance in the body.
Key Processes Involved:
- Protein Synthesis: Steroids increase the rate at which muscle cells produce new proteins, leading to hypertrophy (muscle growth).
- Nitrogen Retention: By improving the nitrogen balance, steroids create an optimal environment for muscle repair and growth.
- Red Blood Cell Production: Many steroids stimulate erythropoiesis (red blood cell production), enhancing oxygen delivery to muscles and improving endurance.
- Fat Metabolism: Certain steroids promote lipolysis (fat breakdown), making them effective during cutting cycles.
In bodybuilding, this results in faster recovery times, increased strength, and significant muscle growth.
Types of Steroids
Steroids are available in two primary forms: oral steroids and injectable steroids. Each category has its unique features, uses, and benefits in bodybuilding.
Oral Steroids
Oral steroids come in tablet or capsule form, making them convenient and easy to use. However, they are metabolized by the liver, which can lead to strain on this organ if not used responsibly.
Popular Oral Steroids:
- Dianabol (Methandrostenolone) : A powerful bulking steroid that rapidly increases muscle mass and strength.
- Anavar (Oxandrolone) : Known for its fat-burning properties, Anavar is a go-to for cutting cycles and lean muscle retention.
- Winstrol (Stanozolol) : Improves muscle definition and strength without water retention.
- Anadrol (Oxymetholone) : Known for its ability to rapidly increase muscle mass and strength, making it a popular choice among bodybuilders.
Injectable Steroids
Injectable steroids are administered via intramuscular injection and are preferred by many athletes for their longer duration of action and reduced liver toxicity.
Popular Injectable Steroids:
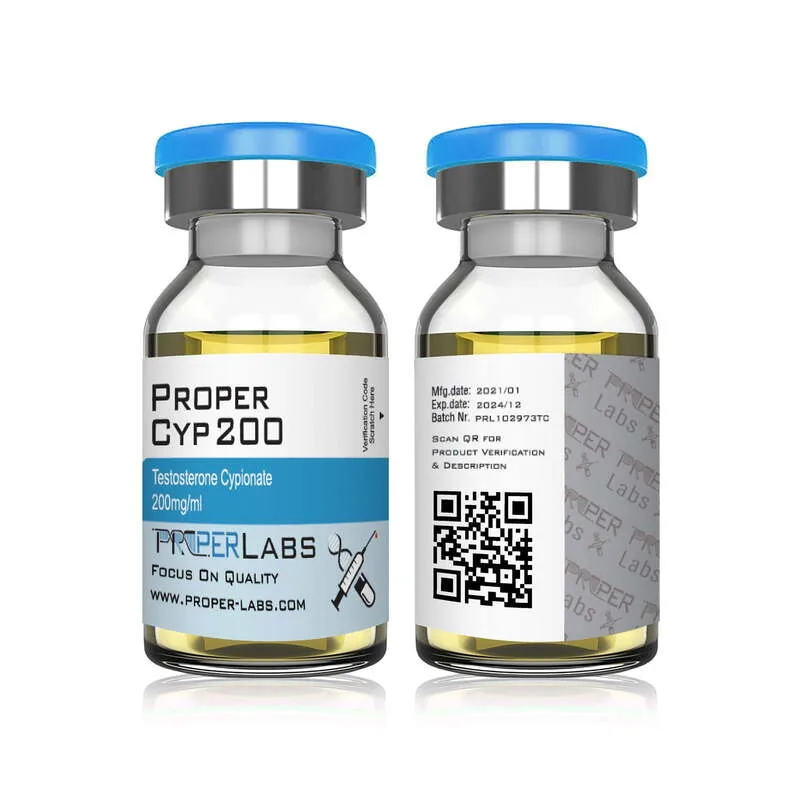
- Testosterone Cypionate/Enanthate : Base steroids for bulking cycles, promoting muscle size and strength.
- Deca Durabolin (Nandrolone Decanoate) : Known for its joint-supporting properties, making it a favorite among bodybuilders.
- Trenbolone Acetate : A powerful anabolic for cutting, offering dry, lean muscle gains and enhanced vascularity.
- Equipoise (Boldenone Undecylenate) : Enhances appetite and protein synthesis, ideal for lean muscle building.
Benefits of Steroids
| Muscle Growth Steroids dramatically increase muscle size by enhancing protein synthesis and nitrogen retention. This makes them effective for athletes aiming to bulk up. | Strength Gains By increasing red blood cell production and ATP synthesis, steroids improve overall strength and stamina. | Fat Reduction Certain steroids, like Anavar and Winstrol, promote fat loss while preserving lean muscle, making them ideal for cutting cycles. |
| Faster Recovery Steroids speed up muscle recovery by reducing inflammation and improving cellular repair, allowing for more frequent and intense training sessions. | Enhanced Endurance Improved oxygen delivery through increased red blood cells enhances endurance during prolonged workouts or competitions. | Improved Definition Cutting steroids helps athletes achieve a lean, vascular appearance by eliminating water retention and enhancing muscle hardness. |
Steroid Cycles and Stacking
Experienced bodybuilders follow structured anabolic steroid cycles to achieve optimal muscle growth while minimizing side effects. A cycle typically lasts between 6-12 weeks, followed by a rest period to allow the body to recover and stabilize its natural hormone levels.
- Bulking Cycles : For bulking cycles, steroids like Testosterone, Dianabol, Deca-Durabolin, and Anadrol are common. These compounds promote rapid muscle growth, increased strength, and enhanced recovery, helping users achieve significant size gains in a short time.
- Cutting Cycles: Popular choices for cutting include Anavar, Winstrol, Trenbolone, and Masteron. These steroids focus on fat loss, muscle definition, and a dry, vascular appearance while preserving lean muscle tissue.
- Stacking Steroids: Advanced users often “stack” multiple steroids in the same cycle to create synergistic effects. For example:
- A basic bulking stack might combine Testosterone with Dianabol.
- A more advanced stack could include Testosterone, Deca-Durabolin, and Trenbolone.
- Cutting stacks may involve Winstrol, Anavar, and Masteron for defined, lean results.
Stacking requires careful planning to balance benefits with potential side effects. Compounds are selected based on how they work together, with dosages adjusted to match the user’s experience level and specific goals.
Designing cycles and stacks also requires a thorough understanding of steroid properties, interactions, and timing. Beginners should start with straightforward, single-compound cycles and gradually explore more advanced stacks as they gain experience and knowledge.
Post Cycle Therapy (PCT) in Steroid Cycles
Post Cycle Therapy (PCT) helps the body recover from the suppression of natural testosterone caused by anabolic steroid cycles. It is a vital step to restore hormonal balance, especially after cycles involving higher dosages or lasting longer than a month. The primary goals of PCT include:
- Promoting overall recovery : Helping the body transition back to its natural state, both hormonally and physically.
- Preserving muscle gains : Maintaining the hard-earned muscle mass and strength achieved during the steroid cycle.
- Preventing hormonal imbalances : Reducing estrogen-related issues like gynecomastia and mood swings.
- Supporting testicular function : Preventing or reversing testicular atrophy and promoting reproductive health.
- Reducing catabolic effects : Preventing muscle breakdown and the rise of cortisol levels, which can harm recovery and performance.
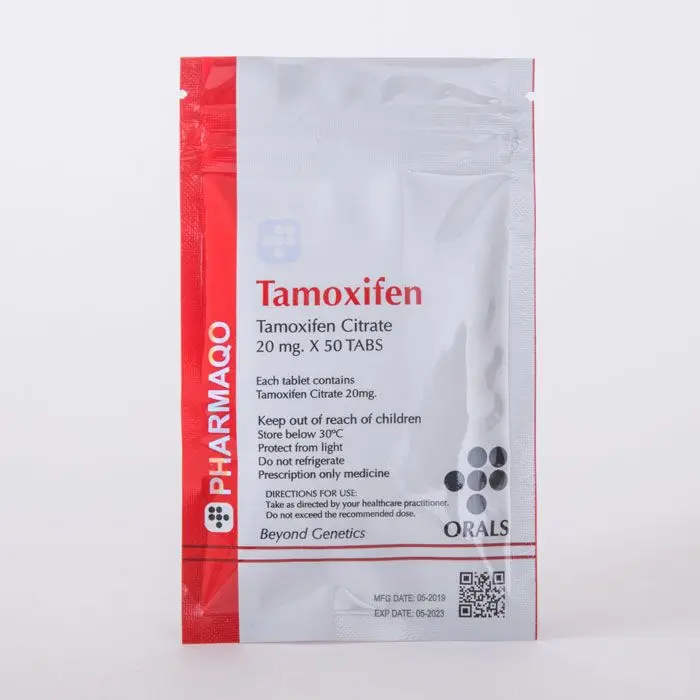
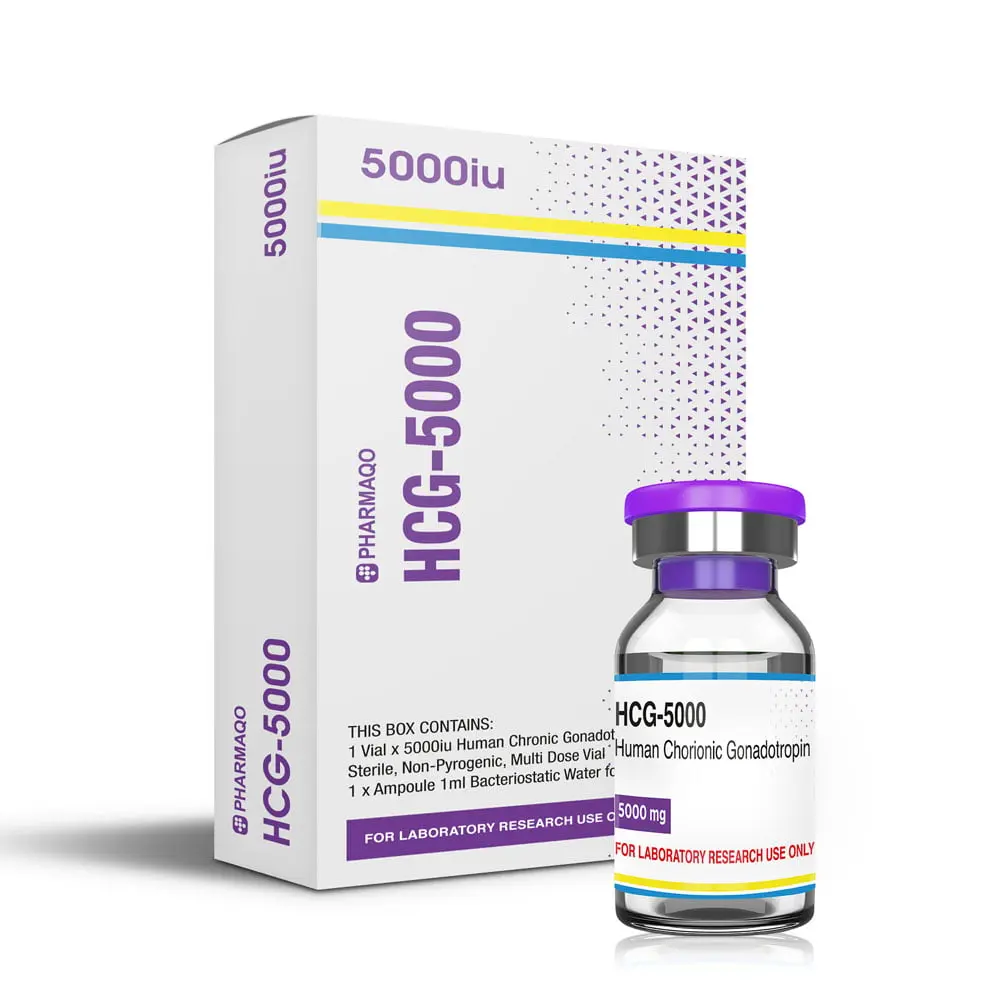
The most commonly used PCT supplements are Clomid , Nolvadex , and HCG . These compounds stimulate the pituitary gland to produce luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which are necessary for natural testosterone production. Aromatase inhibitors (AIs) like Arimidex may also be included to address estrogen-related concerns during recovery.
PCT protocols typically last between 4 to 6 weeks and should start shortly after the steroid cycle ends, depending on the compounds used. For shorter-acting steroids, PCT may begin within a few days, while longer-acting ones may require a delay of up to two weeks.