Remember! Testosterone Enanthate is a prescription medication that requires a doctor's approval. It has been approved by the FDA for treating low testosterone levels, but using it without proper medical supervision can be unsafe and illegal. As with any medication, discuss the potential risks and benefits with your healthcare provider.
How Testosterone Enanthate works?
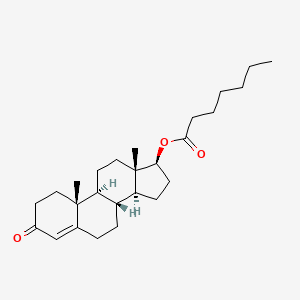
Testosterone Enanthate is a type of testosterone medication that bodybuilders often use to build muscle and boost strength. It is a man-made version of the testosterone hormone that the body naturally produces.
When injected into the muscle, Testosterone Enanthate slowly releases testosterone into the bloodstream over 1-2 weeks. This provides a steady supply of extra testosterone to the body.
Here's how it works for bodybuilding:
Testosterone helps build muscle by increasing protein synthesis - the process of repairing and growing new muscle tissue. With more testosterone, muscles can grow bigger and stronger from weightlifting.
It also promotes nitrogen retention in the muscles. Nitrogen is needed to build more protein than the body breaks down during intense training. Read more
Additionally, testosterone increases red blood cell production to deliver more oxygen to the muscles. This improved oxygen supply can enhance muscular endurance.
While effective for bodybuilding goals, it's important to follow dosage guidelines from medical professionals. Using too much or without proper monitoring can lead to side effects like acne, hair loss, and increased risk of sleep apnea according to medical studies.
Getting regular bloodwork to check testosterone levels is recommended when using this medication for bodybuilding purposes. Consulting trusted medical sources is essential for safe and responsible use.
Testosterone Enanthate Benefits & Features
Features:
- Long-acting testosterone ester
- Slower release into the bloodstream
- Less frequent injections required (every 1-2 weeks)
Benefits:
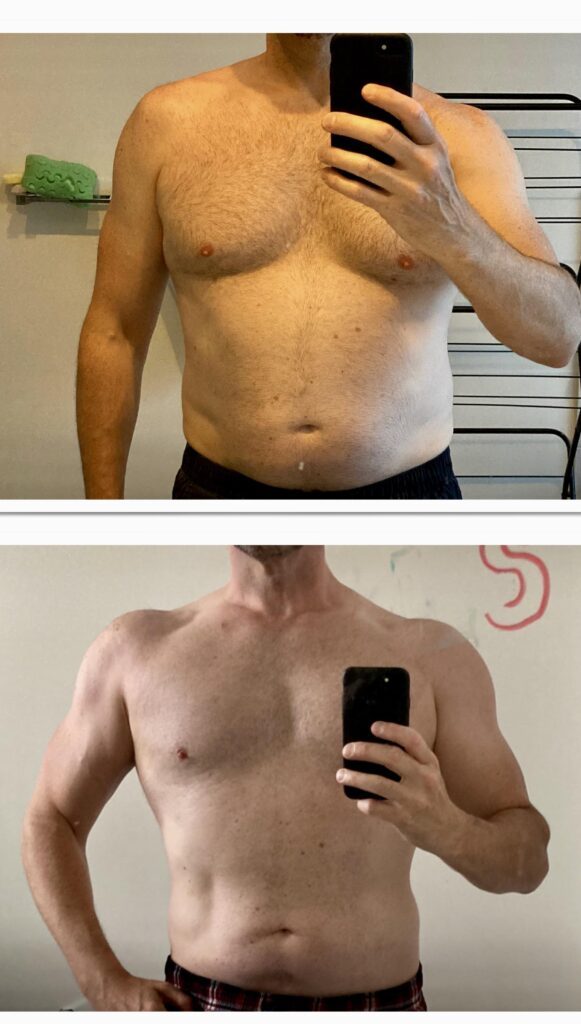
Increased Muscle Mass and Strength: As an exogenous testosterone source, Testosterone Enanthate enhances protein synthesis, nitrogen retention, and the release of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), leading to significant gains in lean muscle mass and strength.
Improved Body Composition: Testosterone Enanthate can help reduce body fat levels while preserving lean muscle tissue, resulting in a more sculpted and defined physique.
Increased Red Blood Cell Production: By stimulating erythropoiesis, Testosterone Enanthate can increase red blood cell count, leading to improved oxygen transportation and enhanced endurance during training.
Faster Recovery: Testosterone plays a crucial role in muscle repair and recovery, allowing bodybuilders to train harder and more frequently without excessive fatigue or soreness.
Improved Libido and Mood: Adequate testosterone levels are associated with increased sexual desire and improved overall mood, which can positively impact motivation and adherence to a rigorous bodybuilding regimen.
Joint Relief: Testosterone Enanthate can help alleviate joint pain and stiffness, which is common among bodybuilders due to the high-impact nature of their training. By reducing inflammation and promoting collagen synthesis, it can improve joint health and mobility, allowing for more intense workouts.
Enhanced Nutrient Partitioning: Testosterone Enanthate can positively influence nutrient partitioning, meaning it can direct more of the calories consumed towards building lean muscle mass rather than being stored as fat. This can be beneficial for bodybuilders during bulking phases, as it maximizes the anabolic effects of their surplus caloric intake.
Increased Vascularity: One of the aesthetic benefits of Testosterone Enanthate is its ability to improve vascularity, or the visibility of veins, particularly in the arms and shoulders. This can contribute to a more defined and muscular appearance, which is highly desirable in bodybuilding competitions.
Cardioprotective Effects: Contrary to some misconceptions, appropriate use of Testosterone Enanthate can potentially offer cardioprotective benefits, such as improving lipid profiles and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases, which is important for maintaining overall health during intense training regimens.
Increased Bone Density: Testosterone Enanthate can help promote bone mineral density, which is crucial for bodybuilders who subject their skeletal system to significant stress during heavy lifting. This can reduce the risk of bone-related injuries and improve overall structural strength.
Testosterone Enanthate Dosage
When it comes to using Testosterone Enanthate for bodybuilding, getting the dosage right is very important! This synthetic testosterone has to be carefully administered under medical supervision or professional bodybuilders care to be safe and effective.
For bodybuilders, typical doses range from 300-600mg per week, split into 1-2 injections. However, it's important to start with a lower dose, around 200-300mg per week, to assess your body's response.
For Men:
Beginners:
- 200-300mg per week
Intermediate/Semi-Advanced:
- 300-500mg per week
Advanced/Professionals:
- 500-800mg per week
For Women:
- Testosterone is not commonly used by female bodybuilders due to virilization risks
Dosing Protocols:
- Injections are typically given 1-2 times per week to maintain stable levels
- Dosages are cycled, using for 8-16 weeks followed by 4-8 weeks off
- Doses are split into smaller injections throughout the week (e.g. 500mg split into 2x250mg)
The dosage is usually cycled, with 8-16 weeks of use followed by 4-6 weeks off to allow the body to recover normal testosterone production. Exceeding recommended doses or cycling too long increases the risk of side effects.
Exact dosages need to be calculated based on individual goals, experience levels, and bloodwork monitoring. Following dosage guidelines from qualified healthcare providers or experienced bodybuilding professional is extremely important for safe and effective use of testosterone enanthate for bodybuilding.
Testosterone Enanthate Cycle
It's important to note that these are general recommendations, and individual factors such as age, fitness goals, and overall health should be considered. Additionally, proper medical supervision and guidance from a qualified healthcare professional or experienced bodybuilder are essential when undertaking any anabolic steroid cycle.
If You're looking for special cycle recommendations, made personally for You - contact us! Our experienced team will help You in Your Testosterone Enanthate Cycle.
| Week | Supplement | Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Testosterone Enanthate | 300mg |
| 2 | Testosterone Enanthate | 300mg |
| 3 | Testosterone Enanthate | 300mg |
| 4 | Testosterone Enanthate | 300mg |
| 5 | Testosterone Enanthate | 450mg |
| 6 | Testosterone Enanthate | 450mg |
| 7 | Testosterone Enanthate | 450mg |
| 8 | Testosterone Enanthate | 450mg |
| 9 | Testosterone Enanthate | 600mg |
| 10 | Testosterone Enanthate | 600mg |
| 11 | Testosterone Enanthate | 300mg |
| 12 | Testosterone Enanthate | 300mg |
| 13 | None | 0 |
| 14 | None | 0 |
| 15 | Start Post Cycle Therapy (PCT) | Personally |
Testosterone Enanthate Side Effects
Common side effects may include acne, hair loss, increased aggression, and fertility issues. More serious risks like sleep apnea, liver strain, and negative impacts on cholesterol levels are also possible!
Common Side Effects:
- Acne and oily skin
- Hair loss
- Increased body hair growth
- Aggression/Irritability
- Decreased sperm count/Fertility issues
More Serious Risks:
- Sleep apnea
- Liver strain/Dysfunction
- Negative impacts on cholesterol levels
- Enlarged prostate in older men
- Increased risk of blood clots
The severity and likelihood of these side effects often depends on the dosage and cycle length. Higher doses and longer, uninterrupted cycles increase the risks. Read more about Side effects
To reduce these risks, it's crucial to carefully follow dosage protocols outlined by qualified healthcare professionals experienced in supervised testosterone therapy. Never exceed recommended doses or cycle lengths.
Getting regular bloodwork is highly advised to monitor testosterone levels as well as liver and kidney health markers. This allows doses to be adjusted as needed.
Lifestyle factors can also help minimize side effect risks. A clean, high-protein diet supports healthy hormone levels. Supplements like milk thistle may provide liver protection.
Proper exercise, stress management, and ensuring adequate sleep and hydration will also support the body's ability to process and respond well to the medication.
Open communication with your doctor about any side effects is important for adjusting protocols safely. Using only pharmaceutical-grade high quality testosterone enanthate from reliable sources is strongly recommended to avoid contaminated products.
While side effects are possible, being well-informed about the risks and following medical guidance can help users maximize the bodybuilding benefits of Testosterone Enanthate responsibly.
If You're looking for any help or advice about Testosterone Enanthate side effects - contact us via live chat or email for free professional advice!Testosterone Enanthate Stacks
When using Testosterone Enanthate, combining it with other supplements or medications in what's known as a "stack" can potentially enhance its effects while helping to control side effects. Here are some common stacking options:
For Bulking and Muscle Gains: Stacking testosterone with compounds like Deca-Durabolin (nandrolone) or Dianabol (methandrostenolone) can lead to greater gains in muscle mass and strength when bulking up.
- Stack with compounds like Deca-Durabolin (Nandrolone) at 200-600mg/week or Dianabol (Methandrostenolone) at 20-50mg daily
- Cycle length of 12-16 weeks is common when stacking for bulking
- AI like Arimidex may be needed to control estrogen
- On-cycle support supplements like milk thistle are recommended
For Cutting and Fat Loss: Adding anabolic compounds like Trenbolone, Winstrol (stanozolol), or Anavar (oxandrolone) to a testosterone base can help preserve lean muscle while getting leaner.
- Add in compounds like Trenbolone at 200-400mg/week, Winstrol at 25-50mg daily, or Anavar at 40-80mg daily
- Cutting cycles are usually run for 8-12 weeks
- AI and on-cycle support are typically used as well
For Boosting Free Testosterone: Aromatase inhibitors like Arimidex (anastrozole) can prevent testosterone from being converted to estrogen, keeping more of it in its active "free" form.
- Aromatase inhibitors like Arimidex at 0.5-1mg every other day
- Can be run for the duration of a cycle to maximize free/active testosterone
Managing Side Effects: Supplements like Cabergoline can help control prolactin levels and related side effects like leaky nipples. HCG injections may help maintain natural testosterone production during cycles.
- Cabergoline at 0.25-0.5mg 2x/week to control prolactin
- HCG at 250-500iu 2-3x/week to maintain natural production
- Cycle support like NAC at 600-1200mg daily to aid liver/kidney function
Stack 1: Testosterone Enanthate and Arimidex (Anastrozole)
| Week | Testosterone Enanthate | Arimidex (Anastrozole) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 500mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 2 | 500mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 3 | 500mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 4 | 500mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 5 | 500mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 6 | 500mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 7 | 500mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 8 | 500mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 9 | 500mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 10 | 500mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 11 | 500mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 12 | 500mg | 0.5mg every other day |
Stack 2: Testosterone Enanthate, Dianabol (Methandrostenolone), and Nolvadex (Tamoxifen)
| Week | Testosterone Enanthate | Dianabol | Nolvadex |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 500mg | 30mg | - |
| 2 | 500mg | 30mg | - |
| 3 | 500mg | 30mg | - |
| 4 | 500mg | 30mg | - |
| 5 | 500mg | - | - |
| 6 | 500mg | - | - |
| 7 | 500mg | - | - |
| 8 | 500mg | - | - |
| 9 | - | - | 20mg |
| 10 | - | - | 20mg |
| 11 | - | - | 20mg |
| 12 | - | - | 20mg |
Stack 3: Testosterone Enanthate, Trenbolone Enanthate, and Arimidex (Anastrozole)
| Week | Testosterone Enanthate | Trenbolone Enanthate | Arimidex (Anastrozole) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 500mg | 400mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 2 | 500mg | 400mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 3 | 500mg | 400mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 4 | 500mg | 400mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 5 | 500mg | 400mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 6 | 500mg | 400mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 7 | 500mg | 400mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 8 | 500mg | 400mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 9 | 500mg | 400mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 10 | 500mg | 400mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 11 | 500mg | 400mg | 0.5mg every other day |
| 12 | 500mg | 400mg | 0.5mg every other day |
Testosterone Enanthate Results
Testosterone Enanthate PCT
After a cycle of using Testosterone Enanthate, it's important to follow a proper post cycle therapy (PCT) protocol to help restore your body's natural testosterone production. PCT involves taking supplements that stimulate and support this process. Here's what you need to know:
When to Start PCT You'll want to begin PCT roughly 2-3 weeks after your last Testosterone Enanthate injection. This allows time for the exogenous testosterone levels to leave your system.
Common PCT Compounds The most common PCT compounds are SERMs (selective estrogen receptor modulators) like Clomid (clomiphene) or Nolvadex (tamoxifen). These help restart your natural testosterone production.
PCT Dosage: A typical PCT run could involve 4-6 weeks of 50mg Clomid daily for the first 2 weeks, followed by 25mg daily for the remaining 2-4 weeks. Some PCT protocols also incorporate HCG injections or an aromatase inhibitor initially.
Standard PCT Protocol:
- Weeks 1-2: Clomid 50mg per day
- Weeks 3-4: Clomid 25mg per day
- Weeks 5-6: Clomid 12.5mg per day (optional)
With HCG Kickstart:
- Weeks 1-2: HCG 1000-2000iu every 3-4 days
- Weeks 3-4: Clomid 50mg per day
- Weeks 5-6: Clomid 25mg per day
Longer Duration PCT:
- Weeks 1-4: Clomid 50mg per day
- Weeks 5-8: Clomid 25mg per day
Dual SERM PCT:
- Weeks 1-2: Clomid 50mg per day, Nolvadex 20mg per day
- Weeks 3-4: Clomid 25mg per day, Nolvadex 20mg per day
- Weeks 5-6: Nolvadex 20mg per day
With Aromatase Inhibitor:
- Weeks 1-2: Clomid 50mg per day, Aromasin 12.5mg every other day
- Weeks 3-4: Clomid 25mg per day
Supporting Supplements Other over-the-counter supplements can provide added support, like zinc, vitamin D3, and anti-estrogens like DIM or 6-bromo. Getting enough calories and rest is also important during PCT.
Monitoring Progress Blood tests can check hormone levels and confirm testosterone is being restored properly during and after PCT. Getting follow-up tests 4-6 weeks after completing PCT provides assurance your levels have normalized.
Testosterone Enanthate Legal-Status
Testosterone Enanthate is a prescription medication, meaning it is illegal to purchase or possess without a valid doctor's prescription. However, the legal status can vary depending on where you live. Here's a look at the legal landscape for this testosterone product:
United States In the US, Testosterone Enanthate is a controlled substance listed under Schedule III of the Controlled Substances Act. This means it has an accepted medical use, but also potential for abuse or dependence.
To legally obtain Testosterone Enanthate, you must have a prescription from a licensed physician who has diagnosed you with low testosterone levels or another medical condition requiring testosterone therapy.
Possessing or purchasing Testosterone without a valid prescription is considered a federal crime that can result in fines and potential jail time.
Canada Testosterone compounds like Testosterone Enanthate are listed under Schedule IV of Canada's Controlled Drugs and Substances Act. As with the US, a doctor's prescription is legally required to purchase or possess these medications.
Other Countries While legal status varies, most countries tightly regulate and restrict anabolic steroid medications like Testosterone Enanthate to prescription use only for legitimate medical purposes under a doctor's care.
Testosterone Enanthate in Sport
Athletes use Testosterone Enanthate to gain a competitive edge by improving their physical capabilities. The substance accelerates recovery from intense training, allowing athletes to train more frequently and intensely, which can lead to improved performance outcomes. Additionally, the psychological boost from enhanced physical performance can increase an athlete's self-confidence and self-esteem, crucial for performing under pressure.
Detection Challenges
Detecting testosterone use is complex due to its endogenous production. Traditional methods like the testosterone to epitestosterone (T/E) ratio test can be circumvented by athletes using various strategies, such as adding epitestosterone to maintain a normal ratio. The T/E ratio test has a threshold of 4-to-1 set by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA), but natural variations and rapid normalization of the ratio post-administration make it difficult to catch dopers. Advanced methods like Carbon Isotope Ratio (CIR) testing can distinguish between natural and synthetic testosterone, but these tests are costly and labor-intensive, typically used only to follow up on suspicious T/E ratios. Despite these methods, athletes continue to find ways to avoid detection, including using masking agents and other drugs.
Detected Cases
Several athletes have been caught using Testosterone Enanthate and other anabolic steroids. Notable cases include:
- LaShawn Merritt (USA): Sprinter banned for 21 months in 2009/2010 for testosterone use
- Karin Mey Melis (Turkey): Long jumper banned for 2 years in 2012 for testosterone use
- Dennis Mitchell (USA): Sprinter involved in the BALCO scandal, admitted to using testosterone and other substances, resulting in a 2-year ban
- Steve Mullings (Jamaica): Sprinter banned for life in 2011 after testing positive for testosterone and furosemide
- Floyd Landis (USA): The cyclist was stripped of his 2006 Tour de France title after testing positive for synthetic testosterone
- Marion Jones (USA): The track and field athlete admitted to using steroids, including testosterone, as part of the BALCO scandal. She was stripped of her Olympic medals and banned from competition
- Tyson Gay (USA): The sprinter tested positive for a steroid precursor in 2013, resulting in a one-year ban and the forfeiture of his silver medal from the 2012 Olympics
- Ryan Braun (USA): The baseball player was suspended for 65 games in 2013 for using performance-enhancing drugs, including testosterone
- Alex Rodriguez (USA): The baseball player admitted to using steroids, including testosterone, during his career and was suspended for the entire 2014 season
- Rashid Ramzi (Bahrain): The middle-distance runner was stripped of his 2008 Olympic gold medal after testing positive for CERA, an EPO variant that boosts testosterone production
- Justin Gatlin (USA): The sprinter tested positive for testosterone in 2006 and was initially banned for eight years, later reduced to four years on appeal.
Testosterone Enanthate Tips & Guide
Injection Technique Enanthate is an oil-based injection that needs to be administered deep into the muscle belly. Using a larger needle gauge like 21-23G x 1-1.5 inches allows the oil to disperse smoothly. Rotate injection sites between major muscle groups like glutes, quads, and delts.
Injection Frequency With its slow-release design, Enanthate only needs to be injected once or twice per week. Many split the dose, injecting half the total on two separate days spaced 3-4 days apart.
Warming the Oil Gently warming the vial by safely running it under hot water can thin out the dense carrier oil, making the injection smoother and less likely to cause bumps or irritation.
Injection Procedures Follow proper injection protocols – ALWAYS! use fresh needles, swab vials and injection sites with alcohol, aspirate to ensure no blood vessel hit, inject slowly and steadily.
Ancillary Meds Have medications like AI's and PCT meds on hand to help control side effects and restart natural testosterone when stopping Enanthate.
Blood Work Regular bloodwork is crucial to monitor testosterone levels, other hormone panels, and health markers while on therapy to ensure proper protocols.
Storage Store Testosterone Enanthate vials at room temperature away from light and moisture. Avoid freezing or excessive heat. Gently roll vials before use to re-suspend the solution.
Testosterone Enanthate FAQ
Testosterone Enanthate is an injectable synthetic version of the primary male hormone testosterone. It is designed for slow-release delivery into the body over a period of weeks.
It is commonly prescribed to treat low testosterone levels in men caused by conditions like hypogonadism, andropause, or hormonal imbalances related to aging or other medical issues.
It is given as an intramuscular injection, typically into the buttocks, thigh, or shoulder muscle. Injections are required every 1-2 weeks to maintain steady testosterone levels.
Restoring healthy testosterone levels can improve sex drive, erectile function, muscle mass, strength, energy levels, mood, and bone density in men with low testosterone.
Yes, it requires a doctor’s supervision. Potential side effects include acne, sleep apnea, enlarged prostate, male fertility issues, polycythemia, and cardiovascular strain if overused.
No, this form of testosterone therapy is only approved and recommended for use in biological males due to its strong androgenic effects which are inappropriate for women.
Dosages are individualized based on a man’s symptoms, blood tests, age, and doctor’s analysis but generally range from 50-400mg per week.
Doctors measure serum total testosterone as well as free testosterone and other hormones like estradiol to properly evaluate therapy results.
Testosterone Enanthate Reviews
55 year old male, prescribed to me about 18 months ago for TRT. My initial T-Level was around 250 with usual symptoms. Started out 1/2cc of 200 mg for about 2 months with no real change in levels or how I felt. Doc increased to 1cc every 2 weeks. Half way through a cycle I'm up around mid/high 600s. As of my blood work last week at the end of a 14 day cycle I was mid 400s. Prior to this I always droped back to the 250 range. My free T-Level is still low (1.66% of 1.6-2.9% scale) but I don't think this drug fixes free T-Levels. Overall I feel better and my libido is great again. If given the choice I'd take 1/2cc every 7 days than 1cc every 14 days to avoid the half life cycle. - webmd.com
Have been on it for 2 years. Have lost 80 lbs and stamina and energy have improved drastically. No side effects, except acne at times. Receive an injection every two weeks. At 51 and having high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol and with the medications I take for those issues, my physician states my health is great. - webmd.com
Positive, much superior to gel or patch...have used 110 mg/ml every ten days, but causes too much hemoglobin requiring 240 phylebotomies in 20 years of use. Testosterone cypionate crystalizes in 10 ml bottles whereas enanthate doesn't. - webmd.com
I am a 45 year old man utilizing 2 cc's a week and I feel Great! No hair loss, libito & erections like I was a kid. In addition, I had previously taken Ambian CR because I couldn't sleep. Within (3) weeks at 2 cc's (2) units in a 5 ml syringe, I was/am sleeping like a baby without the ambian CR! I have further benifited by a dramatic sence of wellbeing. - webmd.com
Testosterone Enanthate Where to buy
Cost in the US The cash price for Testosterone Enanthate typically ranges from $40 to $100 for a 5ml vial (200mg/ml concentration) without insurance. Prices can vary based on pharmacy, location, and whether you use a generic or brand name version.
Insurance Coverage
Many insurance plans will cover part or all of the cost of prescribed Testosterone Enanthate for treatment of conditions like hypogonadism. Your co-pay will depend on your specific plan's coverage for this medication.
US Pharmacy Options You can fill an Enanthate prescription at most large chain pharmacies like CVS, Walgreens, Rite Aid and supermarket pharmacies as well as your local independent pharmacies.
Canada Pricing In Canada, one 10ml vial of generic Testosterone Enanthate 200mg/ml typically costs between $60-$90 CAD when paying out-of-pocket.
Canadian Pharmacies To get Enanthate in Canada, you need a prescription from your doctor which can be filled at pharmacies like Shoppers Drug Mart, Rexall, London Drugs, and many other retail pharmacy chains across provinces.
Online Options There are also legal online pharmacy options to have your Enanthate prescription shipped directly to you after obtaining a telemedicine doctor's approval in states/provinces that allow it. High Quality Testosterone Enanthate can be also bought in our USA & Canada store.
Testosterone Enanthate Alternatives
Testosterone Cypionate A popular injectable alternative with a slightly shorter half-life than Enanthate (8 days vs 10.5 days). Some find Cypionate causes less volatile fluctuations between injection intervals. Dosing is typically every 7-14 days. It tends to be inexpensive and widely available.
Testosterone Undecanoate An oral capsule form that gets absorbed through the lymphatic system rather than the liver. It maintains more stable testosterone levels due to gradual metabolization. However, it can be quite expensive compared to injectable options. It eliminates the need for injections, which some users prefer.
Testosterone Propionate A fast-acting injectable ester with a short 3-4 day half-life. This requires more frequent injections every 2-3 days to maintain steady levels but allows for quicker adjustments to dosing. It clears the system rapidly after stopping usage compared to longer esters.
Testosterone Suspensions (e.g. Omnadren) Contain a blend of different testosterone esters suspended in water rather than an oily base. This provides both fast and extended release components for less peaking/troughing than individual esters alone. Suspensions typically require larger injection volumes.
Transdermal Gels/Patches Topical gels or patches applied daily avoid needles but can transfer residue through skin contact. Gels may be problematic for those with significant body hair. Patches provide a set daily dosage while gels allow dosage adjustment.
Superbol / Superbolan
Test/Mast/Tren 400 | Pharmaqo Labs
Testosterone Enanthate / Testoviron
Testosterone-E 300 | Pharmaqo Labs
Tri-Compound Blend
Fastrip 150 | Pharmaqo labs
Testosterone Blend
Sustanon 250 | Pharmaqo Labs
Testosterone Propionate
Testosterone-P 100 | Pharmaqo Labs
Testosterone Blend / Test 400
Tri-Ester Test 400 | Pharmaqo Labs
Testosterone Cypionate / Testex
Testosterone-C 200 | Pharmaqo Labs
Testosterone Blend 400
Multi-Ester Test 400 | Pharmaqo Labs
Multi API Formula / Androbolan 400