Human Growth Hormone (HGH), a protein produced by the pituitary gland, plays a pivotal role in growth, body composition, cell repair, and metabolism. Its synthetic form is used to treat disorders like growth hormone deficiency. For those requiring HGH therapy, understanding the correct technique for administration is crucial for the treatment’s efficacy and safety. Injecting HGH involves specific protocols that ensure therapeutic benefits while minimizing potential side effects.
Individuals prescribed HGH therapy often have questions about how to properly administer the hormone. The method involves subcutaneous injections, typically into the fat layer beneath the skin. Prior to self-administration, it is essential to receive proper training from a healthcare professional to understand the correct injection process, including preparation, dosing, and site rotation. Ensuring the correct technique for HGH injections not only optimizes the treatment outcomes but also maintains the harmonious functioning of the hormone within the body.
Quick Summary
- Correct HGH injection techniques are vital for treatment efficacy and reducing side effects.
- Training from a healthcare professional is necessary before self-administering HGH.
- Proper HGH administration includes dose preparation and site rotation.
HGH and Its Functions

Human Growth Hormone (HGH) is a biologically critical substance, influencing various bodily functions including growth, metabolism, and energy levels.
The Role of Growth Hormone in the Body
Growth hormone, produced by the pituitary gland, plays a pivotal role in the body. It facilitates growth in children and adolescents and continues to have important effects in adults, sustaining muscle mass and bone density. This hormone also aids in regulating body composition, body fluids, muscle and bone growth, as well as sugar and fat metabolism. It may even have a role in supporting proper heart function.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Growth | Stimulates the growth of bone and cartilage in children. |
| Muscle | Helps in the building and repairing of muscle tissue. |
| Bones | Contributes to bone density and strength. |
| Metabolism | Supports metabolism of fats and sugars. |
| Energy | Linked with energy levels and overall wellbeing. |
Growth Hormone Deficiency in Children and Adults
Growth hormone deficiency occurs when the pituitary gland does not produce enough HGH. In children, this deficiency can lead to stunted growth and delayed puberty. Adults with low levels of growth hormone can experience a decrease in muscle mass, energy, and bone density, which may contribute to a higher risk of fractures. Other symptoms in adults may include an increase in body fat, particularly around the waist, and a feeling of reduced vitality associated with aging.
| Age Group | Impact of Deficiency |
|---|---|
| Children | Stunted growth, increased fat, delayed puberty. |
| Adults | Decreased muscle mass, bone density, energy, and increased fat. |
Consulting Healthcare Professionals

Before initiating human growth hormone therapy, patients should consult healthcare professionals to assess their specific health needs and understand the appropriate treatments.
Diagnosing HGH Deficiency
Healthcare professionals diagnose HGH deficiency through a combination of symptom assessment, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Patients may present with symptoms like decreased bone density or changes in cholesterol levels. A doctor will typically confirm the diagnosis with blood tests that measure growth hormone levels.
Conditions Requiring HGH Therapy
HGH therapy is often prescribed for certain medical conditions that result in growth hormone deficiency. These include, but are not limited to:
- Genetic disorders affecting growth hormone production
- Heart disease, which can be linked to low growth hormone levels
- Kidney disease resulting in growth hormone deficits
- Patients with a history of pituitary tumors
Risks and Potential Side Effects
Healthcare professionals should carefully evaluate the risks and potential side effects of HGH therapy for each patient. Some potential side effects may include:
- Diabetes: Monitoring blood sugar levels is essential as HGH can alter glucose tolerance.
- Cancer: Patients with a history of cancer should discuss the potential risks of HGH therapy with their doctor.
- Increased risk of heart disease and changes in blood cholesterol levels.
Patients must understand the necessity of a doctor’s prescription for HGH, as it helps ensure the correct dosage and administration while monitoring for side effects.
References
- Growth Hormone Deficiency Diagnosis: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279163/
- HGH Therapy and Heart Disease: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3183535/
HGH Injection Protocols
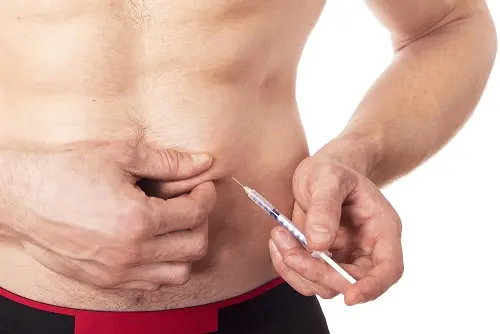
Human Growth Hormone (HGH) therapy necessitates precise protocols to ensure effectiveness and safety. Users must adhere to strict guidelines during preparation and administration stages.
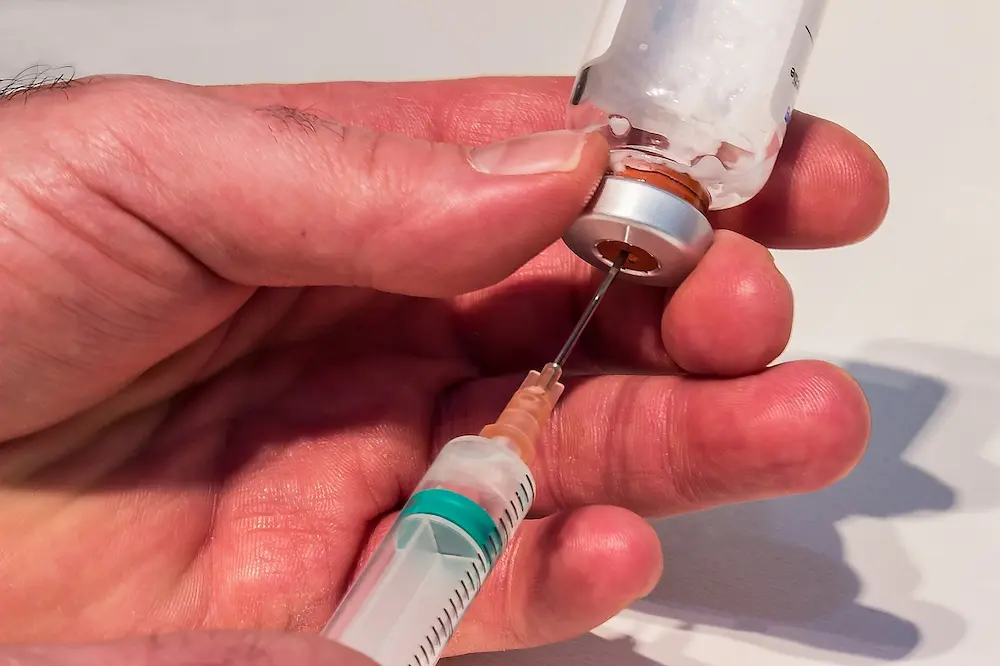
Preparation and Reconstitution of HGH
Before administering HGH, one must prepare the hormone correctly. Reconstitution is the first step, and it involves mixing the powdered HGH (lyophilized form) with a diluent typically provided by the manufacturer. Use sterile syringes and needles to transfer the diluent into the vial containing the HGH powder, and gently swirl the vial to mix. Do not shake the solution as it might cause denaturation of the protein.
Storage is critical post-reconstitution; HGH must be kept refrigerated between 2 to 8 degrees Celsius and away from light. Brands such as Norditropin, Genotropin, and Humatrope provide specific instructions for their products.
Injection Techniques
HGH injections are administered subcutaneously or through intramuscular injection. For subcutaneous injections, typical injection sites include the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. The skin should be cleaned with alcohol, and folds gently to insert the needle at a 45 to 90-degree angle, depending on needle length and personal fat tissue.
Intramuscular injections are less common for HGH and are injected deep into the muscle. They should always be performed with appropriate needle length—usually longer than those used for subcutaneous injections—to reach the muscle tissue.
Frequency and Dosage
The dosage and frequency of HGH injections are prescribed by a healthcare provider and depend on factors such as age, weight, and the condition being treated. HGH is typically injected once daily, although some protocols may call for multiple daily doses or alternate-day dosing.
Dosages are measured in milligrams or international units (IU), and precise dosing is crucial. Overdosing can lead to side effects, while underdosing might render the treatment ineffective. Administration devices like the injector pen can aid in ensuring accurate dosing and simplified administration.
Selecting Injection Sites and Self-Administration
Selecting the correct anatomical sites for subcutaneous injections of HGH is crucial for effective absorption and minimizing side effects. Proper technique in administering HGH at home is equally important to ensure safety and efficacy.
Anatomical Sites for Subcutaneous Injections
Human Growth Hormone (HGH) is typically administered via subcutaneous injection. The primary sites for injection include:
- Abdominal area: At least 2 inches away from the belly button to reduce the risk of irritation.
- Thigh: The front and outer portions are preferred.
- Upper arms: Specifically, the upper posterior regions.
- Lower loins: Avoiding the belt line and any areas of frequent movement.
When injecting into these sites, one should rotate the injection sites to avoid lipoatrophy, a condition where fat tissue is lost, causing indentations in the skin at the site of repeated injections.
Administering HGH at Home
Individuals can administer HGH injections at home after proper training from a healthcare provider. The process includes:
- Handwashing: Essential before preparing the injection to prevent contamination.
- Preparation: Gather all necessary materials — syringe, alcohol swabs, HGH medication, and sharps container.
- Technique: Pinch a fold of skin gently to create an injection site and insert the needle at a 90-degree angle.
Avoiding Complications with Injection Sites
To prevent complications such as bruising, swelling, and lipoatrophy:
- Gently apply pressure after injection without rubbing.
- Do not inject into areas that are tender, bruised, red, or hard.
- Regularly inspect injection sites for signs of infection or changes.
Lifestyle Considerations and HGH Therapy

Successful human growth hormone (HGH) therapy encompasses more than just the hormone injections; it incorporates a holistic approach that includes diet and exercise, which can maximize the efficacy of the treatment. Understanding and managing these factors is key to achieving the desired outcomes in HGH therapy.
Diet, Exercise, and HGH Efficacy
Diet: The consumption of a balanced diet plays a critical role in the effectiveness of HGH therapy. Individuals should focus on a diet rich in proteins, which are the building blocks of muscle tissue, and complex carbohydrates to maintain blood sugar levels. It is essential to minimize the intake of foods with a high glycemic index to avoid spikes in blood sugar that can impede HGH’s effectiveness.
- Proteins: Fish, chicken, tofu, beans
- Complex carbohydrates: Whole grains, vegetables, legumes
Exercise: A regular exercise regimen is crucial to complement HGH therapy. Resistance training can help improve muscle strength, whereas aerobic exercises may assist in weight loss and reducing body fat. Both forms of exercise have the potential to enhance the overall outcome of HGH therapy.
- Resistance training: Weightlifting, pilates, resistance bands
- Aerobic exercise: Running, swimming, cycling
Monitoring Treatment Progress and Adjustments
When undergoing HGH therapy, continuous monitoring of treatment progress is important. Healthcare providers should measure muscle strength and body fat levels periodically to assess the effectiveness of the therapy. Adjustments to the HGH dosage may be necessary based on these results, as well as considerations of any side effects.
Periodic assessments may include:
- Measurement of muscle mass and body fat percentage
- Blood tests to monitor blood sugar levels
Adjustments to the regimen should be made on a case-by-case basis, taking into account the unique responses to the therapy and ensuring the avoidance of performance-enhancing drugs, which are illegal and can adversely affect one’s health.
Frequently Asked Questions

In this section, frequently asked questions regarding Human Growth Hormone (HGH) injections are addressed to clarify dosage, injection techniques, and best practices.
What is the recommended dosage of HGH for enhancing bodybuilding results?
The recommended dosage of HGH for bodybuilding can vary, but it commonly ranges between 1 to 6 IU per day. Healthcare professionals determine the precise dosage based on individual factors such as the user’s goals, health status, and response to the hormone.
What are the best practices for administering HGH in the abdominal area?
When administering HGH in the abdominal area, one should clean the injection site with an alcohol swab and pinch a fold of skin. The injection should be subcutaneous, inserting the needle at a 45 to 90-degree angle. Rotating sites is important to avoid tissue damage.
Is there an optimal thigh location for HGH injections for maximum effectiveness?
The outer, upper thigh is often recommended for HGH injections to ensure maximum effectiveness. This area provides a substantial subcutaneous layer and lessens the likelihood of hitting muscle, which can be more painful.
What is the appropriate needle size for administering HGH injections?
A needle of 29 to 31 gauge and 5/16 to 1/2 inch long is typically appropriate for subcutaneous HGH injections. The small gauge size helps reduce discomfort during injection.
Are there age restrictions for the use of growth hormone injections?
Yes, growth hormone injections are not typically recommended for individuals over the age of 65 or for children who have completed their growth. Prescription HGH is often intended for those with a diagnosed deficiency or specific medical conditions.
What time of day is considered most effective for taking HGH injections?
The most effective time for HGH injections is often in the evening, mimicking the body’s natural growth hormone release patterns. However, some protocols may recommend splitting the dosage into multiple injections throughout the day.
Dr. Grant Fourie, a specialist in male hormones, is based in Cape Town, South Africa. He provides comprehensive treatments for conditions related to low testosterone, such as erectile dysfunction, fatigue, and mood changes. His methods include hormone replacement therapy and other modern treatment options.
Contact me via email or phone to book personal appointment in my clinic: The Village Square, Cape Town - South Africa



